
Trying to figure out, how this wonderful game works, I have not found a single Russian-language manual, so I decided to write my own, where I will describe the basics of gameplay and then, how the pieces move. (This is my first experience writing manuals.)
Introduction.
I really like this game, even if I don't understand much about her, but in this, it seems to me, and her interest lies – learn something completely new and hopefully, that this guide will help you with this at least a little.
The basic rules of the game remain simple and unchanged – checkmate occurs when a player cannot prevent checkmate of at least one of his king.
Measurements.
In ordinary chess (i.e. 2d) involved in all 2 measurements – X и Y, horizontal and vertical movements, respectively. In the same game, technically only 4 measurements (but not 5 (but, agree, “5d chess” sounds cooler)): habitual X, WITH and measurements time and time. You can move pieces between moves – into the future and the past, and also between timelines / parallel universes.
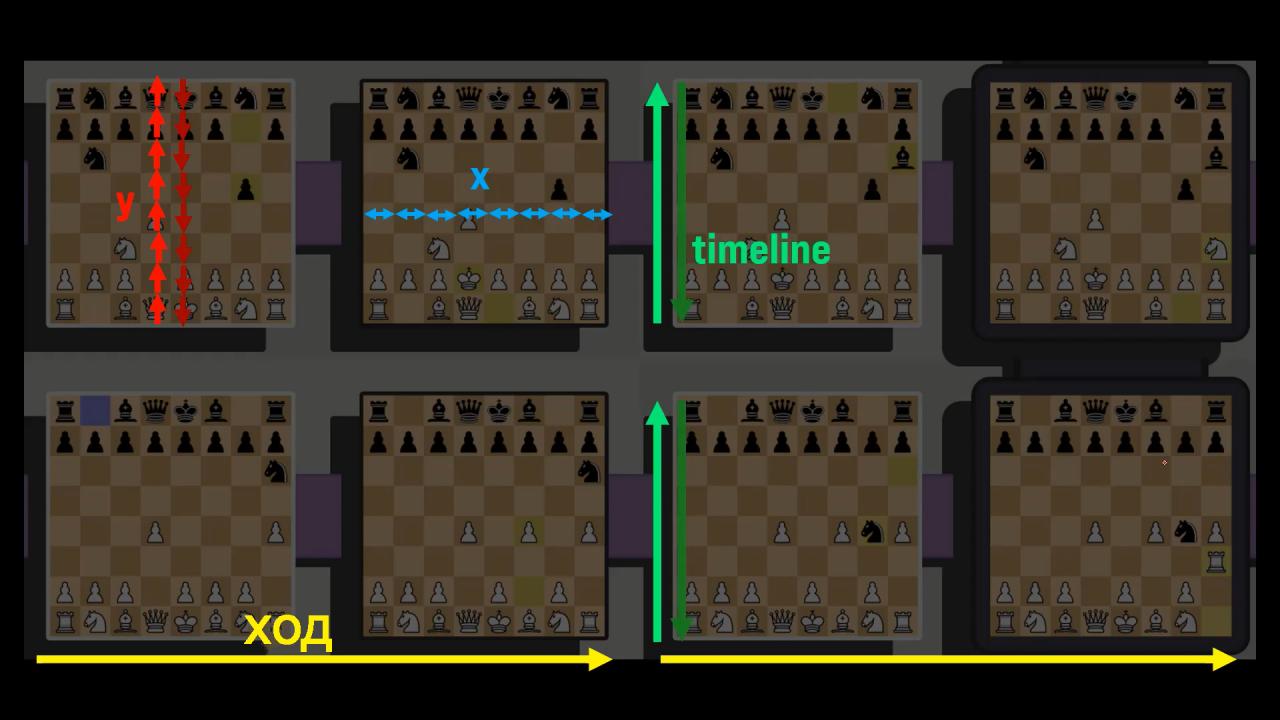
*The move of both players is considered one move..
How time travel works?
In fact, it is impossible to move into the past., since changing the past, the present is changing and any change can destroy everything blabby quantum physics… The point is, what with “moving a figure to the past” another timeline is created, branch from the main (cm. rice. below).
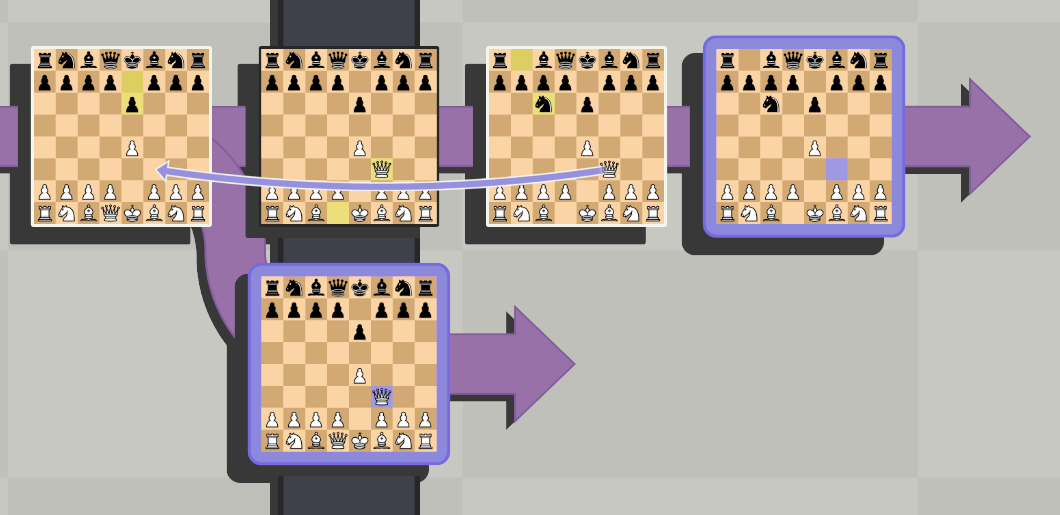 Here the queen is moved to the past and an alternative timeline is created.. (details about moving shapes in time and timelines in the next section)
Here the queen is moved to the past and an alternative timeline is created.. (details about moving shapes in time and timelines in the next section)
Wherein, note, what the present (vertical line along the boards) moves with the moved shape.
- To end your turn, be like all the boards in the present, and you can also (not necessary) move pieces in the future (if there is such a board).
- The past cannot be changed, therefore the easiest way to complete the game – checkmate the opponent's king on the board in the past.
- Whose move is being made on the board can be identified by the color of the board outline (white outline – white move, black – black).
Timeline
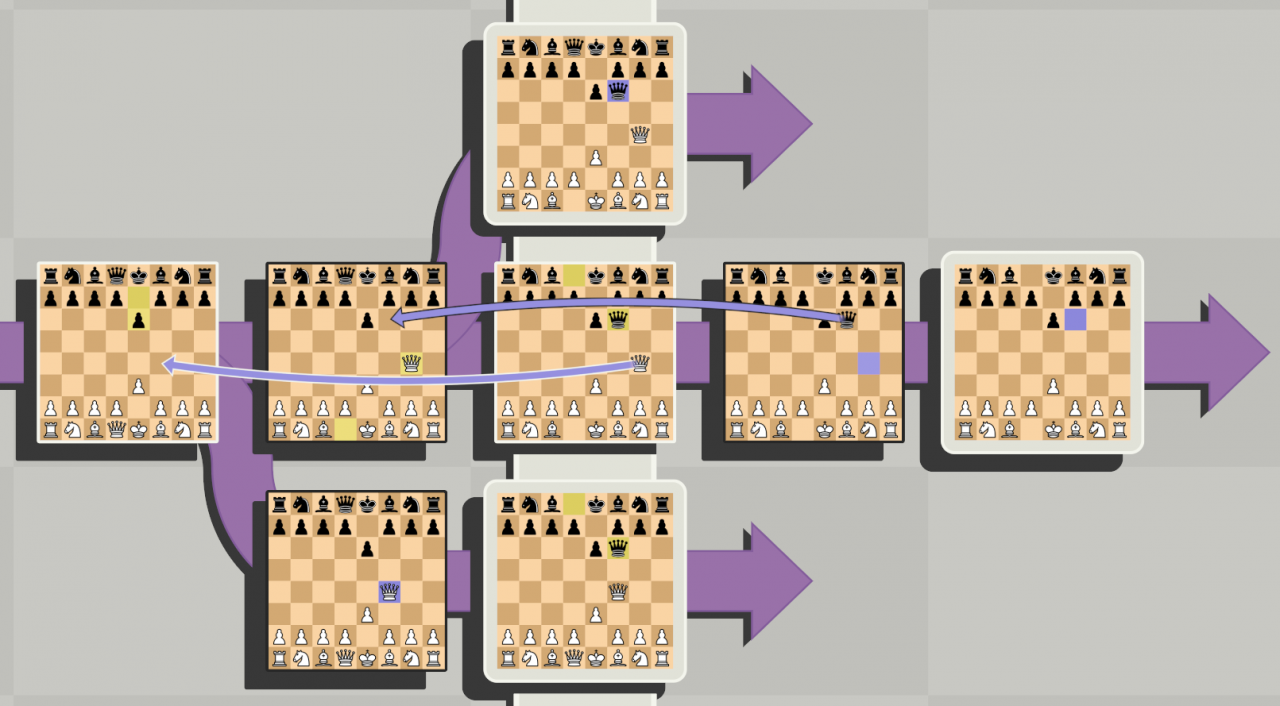
When white moves a piece to the past, “behind the figures” white, a new timeline appears, if black pieces move in time, already “behind their figures” timeline is created (cm. rice. below). (I understand, it can be difficult to perceive these complex pictures, everything will come with practice)
How the pieces move?

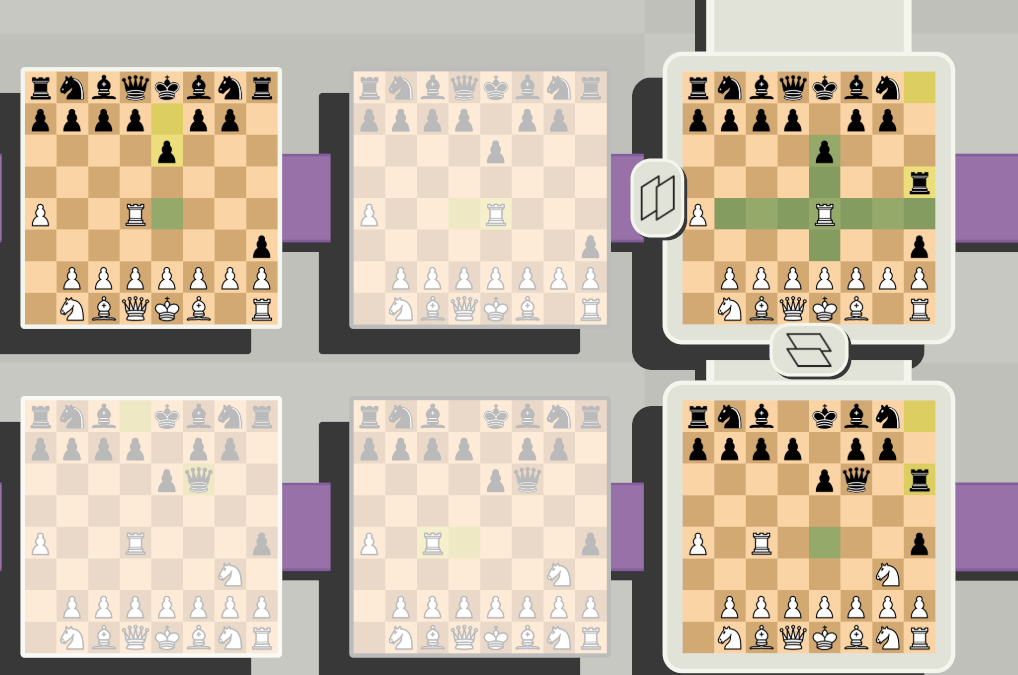 Here the selected rook can move to the previous turn or to another timeline, but at the same time on the board it remains in the same position, since the rook is already moving in one dimension and cannot move in the plane.
Here the selected rook can move to the previous turn or to another timeline, but at the same time on the board it remains in the same position, since the rook is already moving in one dimension and cannot move in the plane.(By the way, by clicking on the icon near the board, you can view all the boards and cells on them, to which the selected shape can move)

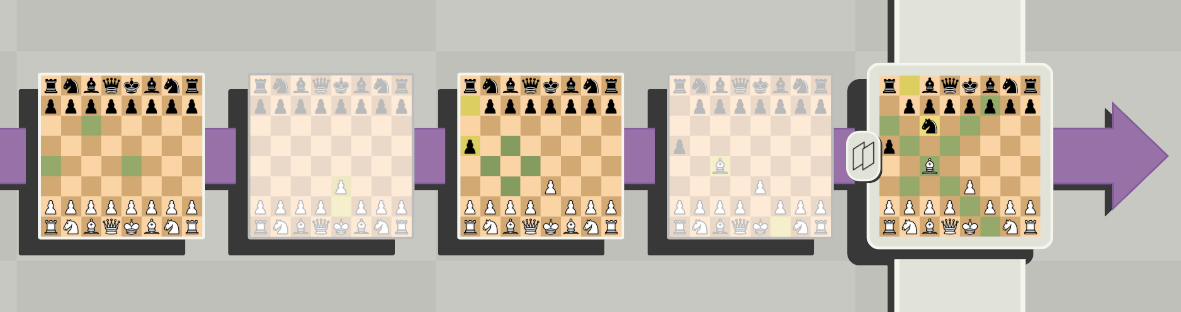 Here the bishop can move n-th number of moves to the past and n-th number of cells along X or Y.
Here the bishop can move n-th number of moves to the past and n-th number of cells along X or Y.





Leave a Reply